
- Description
- Curriculum
- Reviews
Course Description
Algebra—or “al-jabr”— literally means the “reunion of broken parts”. The origin of algebra is traced to the ancient Babylonians and is the unifying thread of almost all of mathematics.
This DSST exam was developed to enable schools to award credit to students for knowledge equivalent to that learned by students taking the course. This exam covers topics such as complex numbers, algebraic operations, equations and inequalities, and properties of functions and their graphs. The use of a non-programmable calculator is permitted in this exam.
Exam Outline
The following is an outline of the content areas covered in the examination. The approximate percentage of the examination devoted to each content area is also noted.
I. Fundamental Algebraic Operations – 20%
- Operations with algebraic expressions
- Operations with polynomials (including factoring and expanding polynomials)
- Rational expressions
- Operations with positive, negative and fractional exponents
II. Complex Numbers – 4%
- Conjugate
- Basic Operations
III. Equations and Inequalities – 44%
- Linear equations and inequalities
- Quadratic equations and inequalities (including quadratic forms and solving quadratic inequalities)
- Absolute value equations and inequalities
- Systems of linear equations and inequalities
- Exponential and logarithmic equations
- Equations involving radicals
IV. Properties of Functions and their Graphs – 32%
- Coordinate systems
- Domain and range
- Operations of functions
- Inverse functions
- Linear functions
- Quadratic functions
- Polynomial functions
- Rational functions
- Exponential and logarithmic functions
Sample Questions
All test questions are in a multiple-choice format, with one correct answer and three incorrect options. The following are samples of the types of questions that may appear on the exam.
1. If x² ≠ 1, then
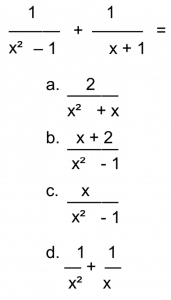
2. Which of the following is a solution of the equation x² + 3x – 2 = 0?
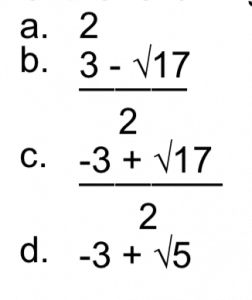
3. An experimental formula for the number of hours of sleep a child needs is S = 13.5 – (y/3), where S is the number of hours of sleep needed and y is the age of the child in years. According to this formula, with each passing year, a child needs:
- 1/3 hour less sleep
- 1/3 hour more sleep
- 1 hour less sleep
- 1 hour more sleep
4.
. 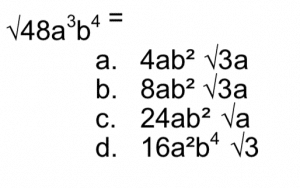
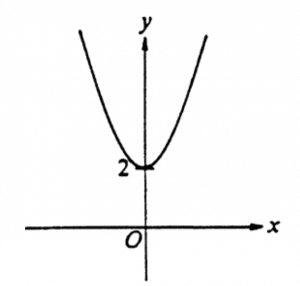
5. Which of the following could be the equation of the graph below?
- y = 2 x2
- y = – x2 + 2
- y = x2 + 2
- x=y2 +2
Answers to sample questions:
1-C; 2-C; 3-A; 4-A; 5-C
-
1INSTRUCTIONS - Please Read
-
2Study Tips
-
3Absolute Value Equations and inequalities
-
4Algebraic Expressions
-
5Algebra of Functions
-
6Complex Numbers
-
7Definition and interpretation of Functions
-
8Determinants
-
9Domain and Range
-
10Exponential and Logarithmic Equations
-
11Exponents
-
12Factorials and Binomial Theorem
-
13Factoring
-
14Graphs and Their Properties
-
15Inverse Functions
-
16Linear Equations and Inequalities
-
17Logarithms
-
18Quadratic Equations and Inequalities
-
19Real Numbers
-
203 WEEKS OUT - Schedule Your Exam
-
21Representation of Functions
-
22Sequences and Series
-
23Systems of Equations
-
24Free Practice Exams
-
25Additional Math Resourses - FREE
-
26Course Videos
-
27Tips For Exam Day
-
28CONGRATULATIONS - FREE Making Education Possible Membership








